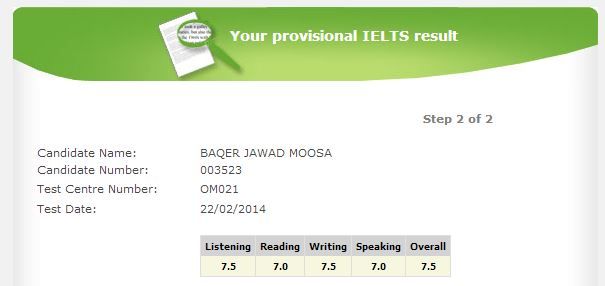
Saturday, 23 February 2013
Monday, 11 February 2013
Heating Systems
Heating Systems in UK
In the UK, various heating methods are provided with minimum cost. Gas is widely used in the UK as a heating method. A gas-fired boiler heats the water and to provide heat through radiators.
A more expensive method to heat is electricity. This involves night storage heates. These use electricity to heat special retaining-heat bricks which will keep homes warm for the day.
In some remote areas where homes are short of mains gas or areas where no main gas is provided, they can always tend to use LPG (Liquid Petrolium Gas). Like the mains gas, it heats the water and provides heat through radiators. Unlike the mains gas, LPG comes in a tank which a person has to buy and could be expensive.
Similar to LPG, rural areas of the country use oil instead. It's probably the same process. Oil-fired boiler heats the water and then the water provides heat through radiators. The oil-tank can be stored above the ground as well as underground.
People can always consider renewable heat by means of solar-energy. It doesn't only generates its own energy but it also reduces carbon print. Renewable sources of energy are very much recommended and people who are less ddependent on sources of energy such as gas and oil are most likely to prefer using these renewable sources.
To know more about how heating systems work in cold countries, watch:-
Thursday, 7 February 2013
Types of Robots
Types of Robots in Car Manufacturing Industry
What is a robot?
A robot is a mahcine which resembles a human being (in a way) and is capable of carrying out a complex series of action.
Coming to car industry, what are the various types of industrial robots used in car manufacturing industry.
Articulated Robots: These kind of robots are greatly flexible with rotary joints. They are used to inspect areas with assembled structures. It is also ued for assmebly, wielding, weld sealing and spray painting.
Cartesian Robots: These are used for pick and place operations, assembly, handling machine tools and arc wielding. They are also called as rectangular co-ordinate robots.
Cylindrical Robots: These kind of robots operate in a cylinder-shaped space. They have a least one rotary joint and at least one prismatic joint. They are used to handle products at die-casting machine, handling machine tools and spot wielding.
Parallel Robots: These kinds of robots have multiple arms each of one has three concurrent prismatic joints. They have large working envelope but are difficult to program and control.
SCARA Robots: SCARA stands for 'Selectively Complaint Arm for Robotic Assembly.These are cylindrical and have two parallel joints. They are also used in pick and place work and assembly operations.
Spherical Robots: These have two rotary joints and one prismatic joint. They are used to handle machine tools and arc or spot wielding.
How Robots Work in car Manufacturing?
To make a robot work, a computer program is installed on its controller computer. This provides a set of precise instructions--based on geometry and carefully timed--that tells the robot where to place things, how to rotate them, where to weld and how to perform all of its other functions. Robots do not think for themselves, and must rely on humans to provide instructions. Robots also can work in more extreme environments on their own, or they can work alongside humans, assisting them in their day-to-day jobs--such as moving or rotating a car so humans can work on parts of it that would normally be difficult to reach
See more about robots in car wheel manufacturing:-
Read more:-
* http://www.globalspec.com/learnmore/manufacturing_process_equipment/manufacturing_equipment_components/robots_robotic_accessories/industrial_robots
* http://www.ehow.com/about_4678910_robots-car-manufacturing.html
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)